Characteristics of an ideal gas- an extremely low concentration- molecules are in a permanent motion- Newton laws can be applied- all collisions are elastic- molecules are spherical- molecules are. One mole of an ideal gas has a volume of 22710947 13 litres at standard temperature and pressure a temperature of 27315 K and an absolute pressure of exactly 10 5 Pa as defined by IUPAC since 1982.

Welcome To Learnapchemistry Com Ap Chemistry Question Paper Ap Chem
The term ideal gas refers to a hypothetical gas composed of molecules which follow a few rules.

. Ideal Gas Molecules STUDY PLAY brownian motion in 1827 botanist Robert Brown noticed that pollen grains in water moved with a zigzag random motion. Ideal gas behaviors -made up of tiny molecules -straight lines random directions -molecules have no attraction -molecules undergo elastic collisions -avg. Chemistry 22062019 0520 anggar20.
Constant volume no intermolecular forces of attraction energy loss in collisions no volume strong intermolecular forces of attraction perfectly elastic collisions constant volume no intermolecular forces of attraction energy gain during collisions no volume no intermolecular. - Exerting a force which causes a pressure. A 10 L sample of a pure gas is found to have a lower pressure than that predicted by the ideal gas law.
Correct statement of ideal gas according to the kinetic-molecular theory of gas a correct. The ideal gas law describes the behavior of real gases under most conditions. In collisions between gas molecules in an ideal gas which of the following best describes the nature of the collision process.
Now up your study game with Learn mode. Neither energy or momentum are conserved. Energy and momentum are conserved.
This is true related to Ideal gas as it is stated in ideal gas theories that molecules are far apart from each other and the actual volume of gas molecules compared to volume of container is negligible. Note for example that N is the total number of atoms and molecules independent of the type of gas Let us see how the ideal gas law is consistent with the behavior of filling the tire when it is pumped slowly and the temperature is constant. High temp low pressure no attraction.
Part A Which of the. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. The ideal gas model tends to fail at lower temperatures or higher pressures when intermolecular forces and molecular size becomes important.
Now we are left with only Option-D In option D it is given that ideal gas has no volume. This type of movement of any particles in a suspension is known as Brownian motion. Which best describes the molecules of an ideal gas Other questions on the subject.
NH 3 molecules are polar while CH 4 molecules are not and the greater attractions between NH 3 molecules cause the molecules to collide with the walls of the container with less force. The volume occupied by gas molecules themselves is not comparable to the volume between the molecu. NH 3 molecules have a greater molar mass than CH 4 molecules so the NH 3 molecules collide with the walls of the container with more force.
Tap card to see definition. C- it is the largest star in. The ideal gas law best describes the properties of which of the following gases at 0C and 1 atm.
Hence for ideal gas Option-D is a correct answer. View the full answer. - Many particles frequently collide with the wall.
What is an elastic collision. Those observation provide evidence that under the given conditions the. Ideal gas law best describes the properties of which of the following gases at 0C and 1 atm.
Why does the sun appear to be the brightest star in the sky. The density of gas in gL is. The best explanation for the observation is that the molecules of the gas.
The same in all 3 containers. B- it burns more gas making it brighter than any other star. Which best describes the molecules of an ideal gas.
You just studied 16 terms. Tap again to see term. A- its apparent brightness is much greater than other stars.
- Pressure ForceArea PFA Click again to see term. Energy and momentum are conserved. Brownian motion with gases.
Kinetic energy of molecules is proportional to the temperature in kelvin -particles are far apart Ideal gas vs Real gas IDEAL. The only interaction between ideal gas molecules would be an elastic collision upon impact with each other or an elastic collision with the walls of the container. The average KE of the gas molecules is.
Ideal gas molecules do not attract or repel each other. It supports the particle theory of the different states of matter.
Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Gases Introductory Chemistry 1st Canadian Edition
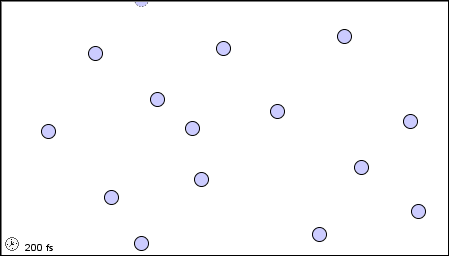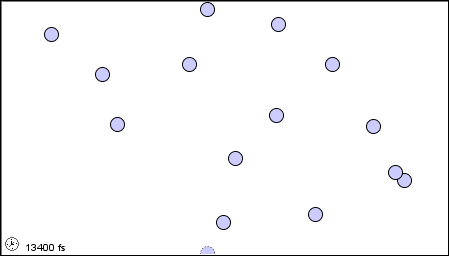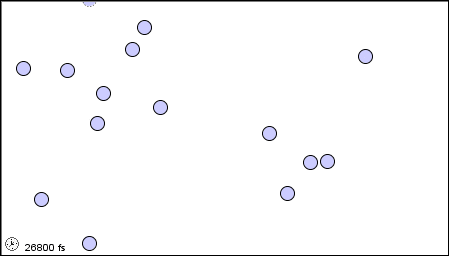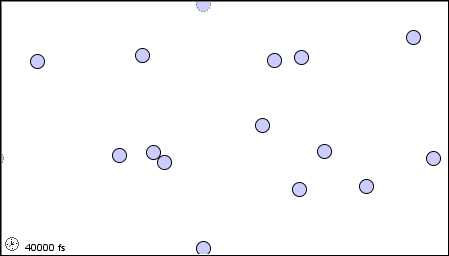
11 1 A Molecular Comparison Of Gases Liquids And Solids Chemistry Libretexts
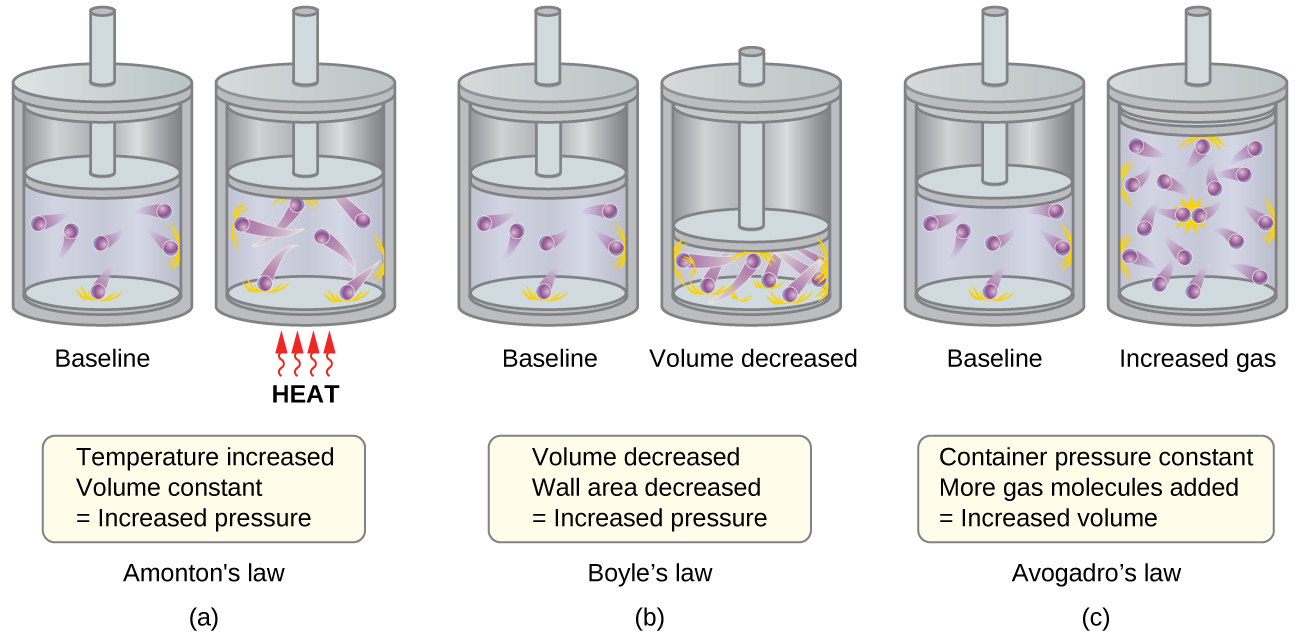
0 Comments